When it comes to connecting modern mass storage devices to old 8 bit computers, the humble compact flash card is ideal. It normally presents itself as a 16 bit IDE drive, although it is quite happy to run in 8 bit mode, and even a small CF card by modern standards can hold a huge amount of data.
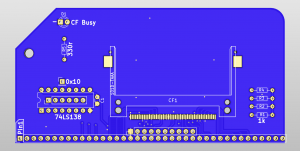
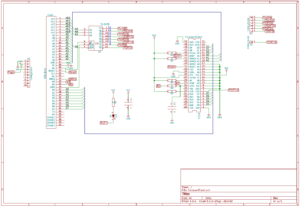
The connections and support circuitry is fairly trivial. Address lines A0, A1 & A2 go directly to the CF card, whilst A3, A4, A5, A6 along with IOREQ and M1 provide the enable signal. RD and WR tell the CF card if it’s a read or write operation and D0 to D7 are connected directly to the data bus. Surplus address lines on the CF card are pulled low and a few other control lines are pulled high via 1k pull up resistors.
To maintain compatibility with Grant Searles Simple CP/M machine, port 16 (0x10) is used to activate the Chip Select 0 line. The other ports from the 74HCT138 are bought out to pads underneath in case there is any need to drive other circuitry
From version 1.2 onward a 100 ohm resistor and 100pf capacitor are added to the RD line. This simple filter increases compatibility with more CF cards than previous versions.
Assembly of the module is fairly straight forward with only 9 components – however, due to the compact flash socket being a surface mount component with pins at 0.025″ (0.635mm) pitch, great care must be taken to avoid solder bridges with this. There are a couple of tiny lugs on the back of the CF socket that locate it exactly on the PCB though, so it should stay perfectly lined up whilst soldering.
For a guide on running CP/M on Compact Flash, see this page.
The files needed can be found on Github
Bill of Materials
- RC2014 CFLASH PCB 1
- Compact Flash Socket 1
- 40 pin RA Header 1
- 16 pin narrow DIL socket 1
- 100nf 1
- 74HCT138 1
- 330R resistor 1
- 1K resistor 4
- 3mm Green LED 1